Associations between prospective symptom changes and slow-wave activity in patients with Internet gaming disorder: A resting-state EEG study
Internet gaming disorder is a newly emerging disorder in which one frequently and uncontrollably plays online games.
Internet gaming disorder is a newly emerging disorder in which one frequently and uncontrollably plays online games. The disorder has similarities to substance use disorders and can lead to clinical deficiencies such as attention deficits, impulsivity, depression and anxiety. In one study, neurophysiological markers related to the symptoms of this disorder were examined using resting-state electroencephalography (EEG).
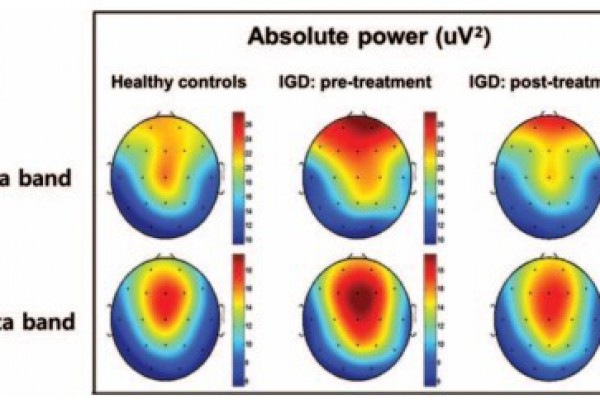
In this longitudinal study, 20 addicted and 29 healthy participants were studied. The addicted group included ones who were being treated on the account of this disorder and its comorbidities. EEG was recorded with eyes open and eyes closed in three phases.The results of data analysis showed a high value of absolute power of the delta band in the frontal area and theta band in the central areas of the brain in baseline in the addicted group. After a six-month treatment period, the absolute power of the delta band in the frontal area in patients was significantly reduced compared to the baseline. This reduction was accompanied by an improvement in the symptoms of the disorder. In addition, the high absolute power of theta in the baseline showed a significant correlation with better improvement of symptoms after treatment.The findings of this study show that the pattern of slow wave activity in people addicted to online gaming who suffer from comorbidities such as depression or anxiety can be used as neurophysiological markers in the treatment process.



Related Posts