Retinal Test a New Prognostic Marker for Multiple Sclerosis Severity
It is essential to assess the severity of multiple sclerosis (MS) in order to choose appropriate therapeutic measures, but this cannot be reliably done using existing methods.
It is essential to assess the severity of multiple sclerosis (MS) in order to choose appropriate therapeutic measures, but this cannot be reliably done using existing methods.
Analyses revealed that retinal layer thinning as a result of an MS relapse predicts the severity of future relapses and, hence, the likelihood of disability.
Researchers led by Gabriel Bsteh and Thomas Berger from the Department of Neurology at MedUni Vienna/University Hospital Vienna, working in collaboration with the Department of Ophthalmology and Optometrics at MedUni Vienna/University Hospital Vienna, studied 167 MS patients over a period of more than three years.
They hypothesized that retinal damage due to relapse reflects the extent of damage in the brain. As the scientific analyses confirmed, the loss of approximately 5 µm (micrometers) of retinal layer thickness after optic neuritis equates to a doubling of the risk of permanent disability after the next relapse.
These predictions could be used as the basis for treatment decisions in future: the results of the study suggest that more aggressive treatment is indicated where there is significant retinal layer thinning than would be the case for a smaller degree of thinning. This is true even if the patient has no disability or only slight disability at the time of measurement.
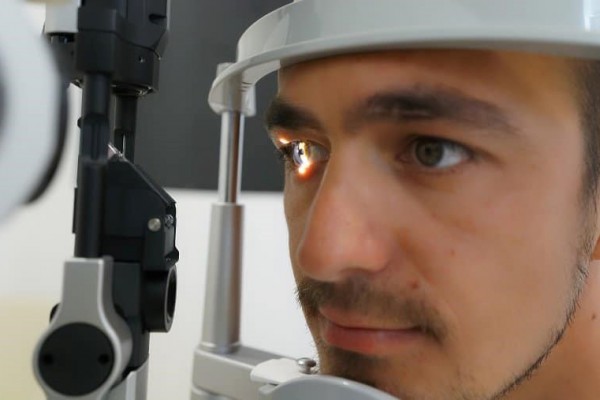
The researchers used optical coherence tomography (OCT) to measure retinal layer thickness. OCT is an imaging technique that uses infrared light to produce high-resolution three-dimensional images of very thin layers of tissue in the micrometer range (1 micrometer=1 thousandth of a millimeter). It is already used as a tool for diagnosing eye diseases such as glaucoma, and for evaluating disease progression.
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease that leads to the loss of axons and neurons throughout the entire nervous system. Although this damage often goes unnoticed by patients at first, its extent determines the prognosis for the severity of the disease.
Since predictions about the course of the disease are important in MS for selecting the appropriate treatment, medical research has long been searching for reliable prognostic tools.
“In retinal layer thickness, we have found a new biomarker that represents a window to the brain, as it were,” said Gabriel Bsteh, summarizing the essence of the study. If the results are confirmed in larger follow-up studies, the technique could also be applied in routine clinical practice.



Related Posts