Concurrent TMS-EEG in NBML
NBML is pioneer to provide the possibility of multimodal brain mapping in the region. In this regard NBML is now able to acquire EEG signal during the TMS brain stimulation. This precise and synchronized recording and stimulation can be used to characterize and study the mechanisms and effects of TMS on brain.
NBML is pioneer to provide the possibility of multimodal brain mapping in the region. In this regard NBML is now able to acquire EEG signal during the TMS brain stimulation. This precise and synchronized recording and stimulation can be used to characterize and study the mechanisms and effects of TMS on brain. The procedure is applicable in fundamental neurobiology researches (Neurobiology) and cognitive neuroscience. This method could also be used in clinical areas, for diagnoses, and monitoring of the brain during the TMS intervention.
The first experiment of concurrent TMS-EEG was successfully conducted on December 4, 2016, in NBML. In this test, the motor area was stimulated with TMS trigger, and several EEG channels from the same area were recorded simultaneously. With the trigger synchronization the time points of TMS stimulation were automatically tagged inside the EEG recording to make the exact analysis and artifact removal possible.
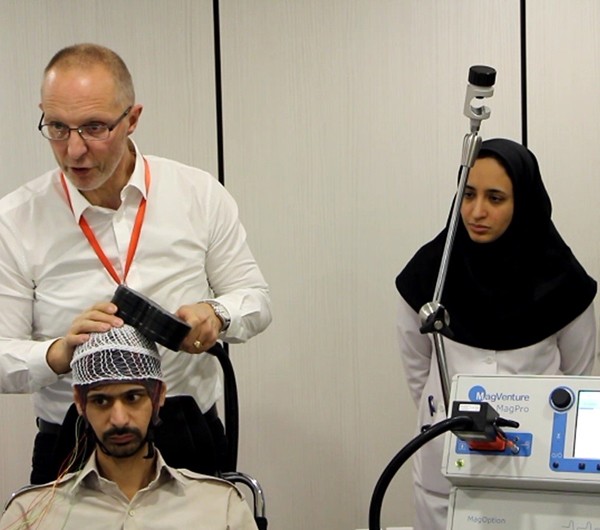
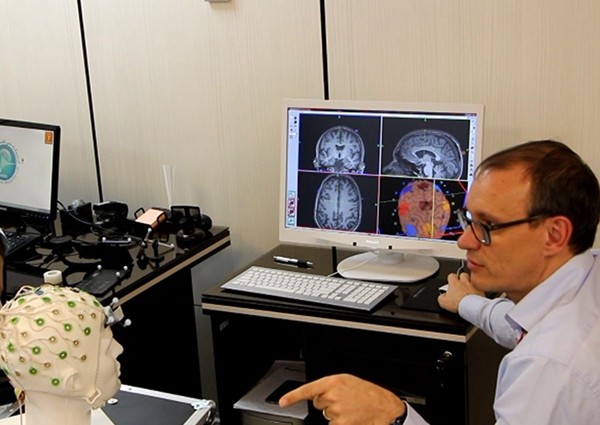
It is also possible to digitize the spatial location of EEG electrodes through the navigation system. This makes the precise analysis and localization of brain sources possible.



Related Posts