Brain activity found to be predictive of pain-related fear
Researchers applied a machine learning technique that could potentially translate patterns of activity in fear-processing brain regions into scores on questionnaires used to assess a patient's fear of pain.
Researchers applied a machine learning technique that could potentially translate patterns of activity in fear-processing brain regions into scores on questionnaires used to assess a patient's fear of pain. This neuroscientific approach, reported in eNeuro, may help reconcile self-reported emotions and their neural underpinnings.
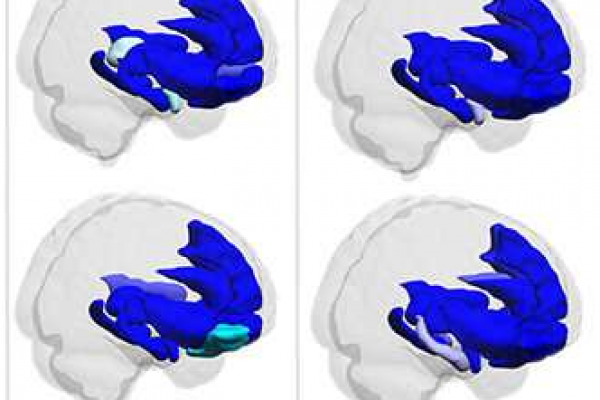
Pain-related fear is typically assessed with various questionnaires, often used interchangeably, that ask patients how they feel about their clinical pain. However, it is unclear to what extent these self-reports measure fear and anxiety, which are known to involve different brain regions, and perhaps other psychological constructs.



Related Posts