آزمایشگاه تصویربرداری تشدید مغناطیسی (MRI)


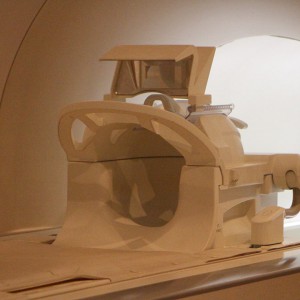








تصویربرداری تشدید مغناطیسی (MRI) یک تکنیک تصویربرداری پزشکی غیرتهاجمی است که برای بسیاری از اهداف از جمله تشخیص بیماری، تعیین میزان پیشرفت یا بهبود بیماری، ارزیابی پاسخ به مداخلات درمانی و… استفاده می شود. روش MRI در سال های اخیر در مطالعات علوم اعصاب جهت بررسی ساختار درونی و عملکرد سیستم عصبی مرکزی نیز کاربرد گسترده ای پیدا کرده است.
تکنیک MRI در سال های اخیر گسترش زیادی پیدا کرده است و با طراحی سکانس های مختلف و متنوع امکان بررسی ساختار و عملکرد مغز به شکل های مختلف مهیا گردیده است.
آزمایشگاه MRI آزمایشگاه ملی نقشه برداری مغز از این قائده مستثنی نبوده و با در دسترس قرار دادن امکانات لازم که مطابق با دانش روز دنیا هستند زمینه تحقیقات را برای محققین این حوزه در سرتاسر کشور فراهم نموده است.
این موارد و تجهیزات لازم برای انجام ازمونها در ذیل بصورت مختصر بیان گردیده است.
کارشناسان این بخش





